Manufacturing Waste Management for Industrial and Hazardous Waste
- RSB Environmental can help you in identifying opportunities to improve the management of industrial and hazardous waste and thus minimize costs and reduce liability.
- Expert in Waste minimization via employee training, material substitutions, recycling, improved management practices, and other best management practices
- Equipt in hazardous and Industrial Waste Management/Permitting.
- Leader in identifying opportunities that helps minimize costs and reduce liability.
Request a free custom quote or call 1-833-910-2535








Testimonial
WHAT OUR RECENT CLIENTS SAY ABOUT US
Sachin and his team at RSB Environmental are very helpful with our company’s environmental needs. Always courteous and informative in regards to our questions.
RSB Environmental is a great company, they are easy to work with and handle all our Environmental needs in a friendly professional way. I would recommend RSB Environmental for all your company’s environmental needs.
Understanding Industrial Waste: Types, Impacts, and Value Creation Through Effective Management
Hazardous and industrial waste, a byproduct of various industrial operations and processes, poses a significant responsibility to manufacturers and facilities due to its potential impacts on the environment and human health. In essence, industrial waste can be any discard from the production process, including paper waste, metal shavings, or chemical sludge. The type and amount of waste produced depend greatly on the industry. For example, a metal fabrication company might have substantial amounts of metal scrap, while a paper mill might generate large volumes of pulp sludge.
Effective waste management can bring substantial benefits to a company, from saving resources and money to reducing environmental impact. For instance, many industries find ways to recycle or repurpose waste materials, which can reduce cost and create value by turning waste into new products. As part of this step, it’s essential to keep an accurate inventory of waste – details such as the type, quantity, and the place where it was generated can offer valuable information. This waste inventory can guide manufacturers in finding the best solution for each type of waste, whether that involves on-site treatment, selling to a recycler, or proper disposal. Furthermore, with people becoming more conscious of environmental responsibility, good waste management practices can bolster a company’s public image and even save money, as fines and cleanup costs associated with improper waste handling can be substantial. However, the process involves complex operations, and companies need to navigate through a maze of regulations and permitting requirements, making it a pertinent question for industry leaders to address.
Hazardous and Industrial Waste Management/Permitting
Hazardous waste generation is an inherent part of most industrial and manufacturing businesses. Waste minimization via employee training, material substitutions, recycling, improved management practices, and other best management practices (BMPs) is a vital part of successfully managing waste and liability.
- RSB Environmental can assist clients with:
- Waste Storage and Management
- Storage Area Design
- Proper waste classification
- Sampling
- Identification
- Manifesting
- Shipment for disposal
- Waste Permit Application
- Waste Management Permit
- Hazardous Waste Management
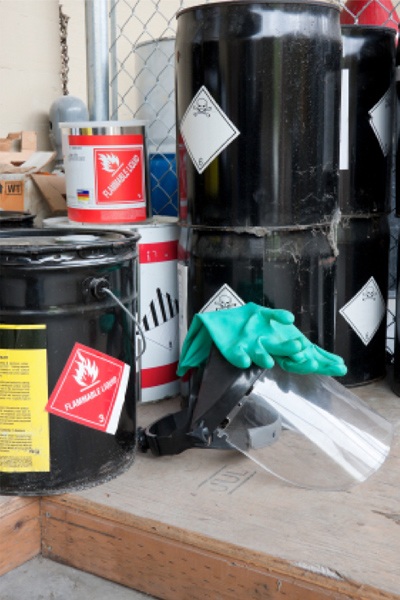

RSB Environmental can also identify opportunities to improve the management of industrial and hazardous waste and thus minimize costs and reduce liability.
WASTE MANAGEMENT SERVICES
- Waste Generation Studies
- Waste Characterization Studies
- Waste Management Plans and Reports
- Program Design, Implementation & Monitoring
- Grant Writing
- Ordinance Preparation & Implementation
- Business Waste Assessments & Technical Assistance
- Rate Studies
- Collection Service & Facility
- Development Procurements
- Privatization Studies
- Hauler Audits
- CD Debris Disposal
- Economic Analyses and Modeling
- Rate Studies
- Solid Waste Collection Services
- Solid Waste Feasibility Studies
- Solid Waste Planning
- Sustainability Services
- Environmental Policy Development LEED® Certification
- Waste Characterization
- Waste Conversion Assessments
- Zero Waste Plans
Our Registrations and Certifications







Frequently Asked Questions
What is considered hazardous or industrial waste?
Hazardous waste is waste that poses significant threats to public health or the environment due to its chemical, physical, or biological properties. Industrial waste is waste produced by industrial activities, such as manufacturing or power generation, and it can be hazardous or non-hazardous.
What is the permitting process for managing hazardous and industrial waste?
The permitting process involves applying to the appropriate regulatory authority (such as the EPA in the U.S.) for permission to generate, store, treat, or dispose of hazardous waste. The permit will specify how the waste must be managed to protect human health and the environment.
Why is waste minimization important in industrial settings?
Waste minimization reduces the volume and toxicity of waste produced, which can decrease disposal costs, conserve resources, and reduce potential harm to human health and the environment.
How are hazardous and industrial waste management facilities regulated?
These facilities are regulated through laws like the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the U.S., which requires them to track their waste from creation to disposal (the “cradle-to-grave” approach), among other things.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with hazardous and industrial waste management regulations?
Non-compliance can result in penalties, including fines, cleanup costs, and potential criminal charges. Additionally, it can harm the company’s reputation, impacting its relationship with customers, investors, and the community.
Industrial Hygiene

Engineering

Safety

Environmental Compliance




